Localization
Localization is a method of tracking the robot's location within an existing map. It is generally done using laser scan data from a 2D LIDAR, and the robot's odometry. For this demo we are using the Nav2 package launch localization.
See the sample robot.yaml for configuration details.
Make sure you have installed the simulator before starting this tutorial. Take a look at the installation guide for details.
Launching Localization
See Launching Nav2 for instructions on launching localization
When using the simulation, it is important to add use_sim_time:=true to the Nav2, SLAM, and
Localization launch files. When using a physical robot, either omit use_sim_time or set it
to false.
Setting the 2D Pose Estimate
When starting localization, the robot will be lost -- no transform from base_link to the map frame will be published.
To fix this you must manually set an initial 2D pose estimate.
The 2D Pose Estimate tool in Rviz allows you to provide Nav2 with the robot's approximate initial position on the map.
This is a necessary step before you can navigate with the robot.
This step connects the map frame to the rest of the robot's TF tree.
To set the robot's initial position, click and hold the mouse button on the map in the robot's approximate location.
While holding the left mouse button, drag the green arrow to set the robot's orientation. Releasing the left
mouse button will set the robot's position and orientation relative to the map frame.
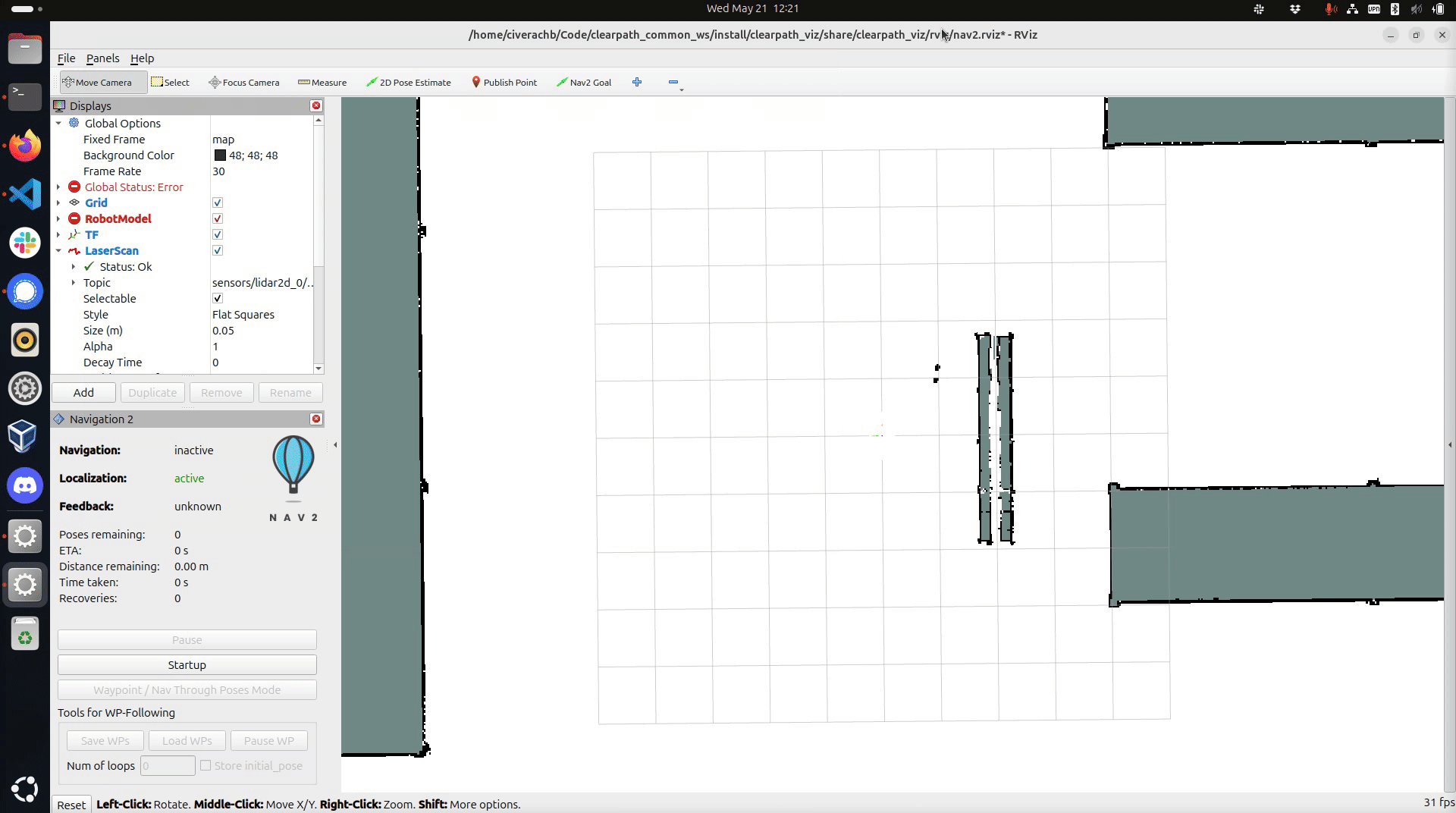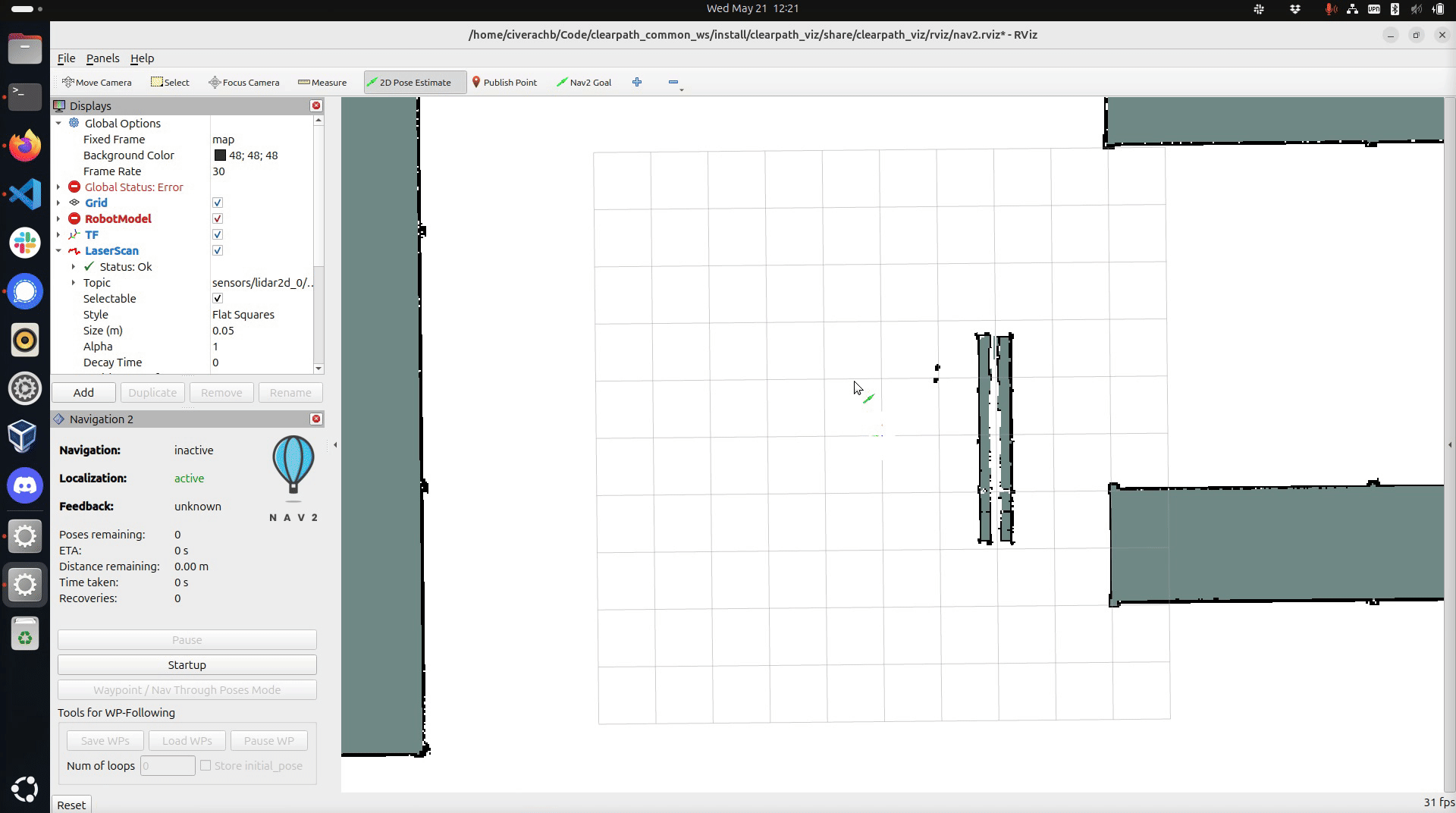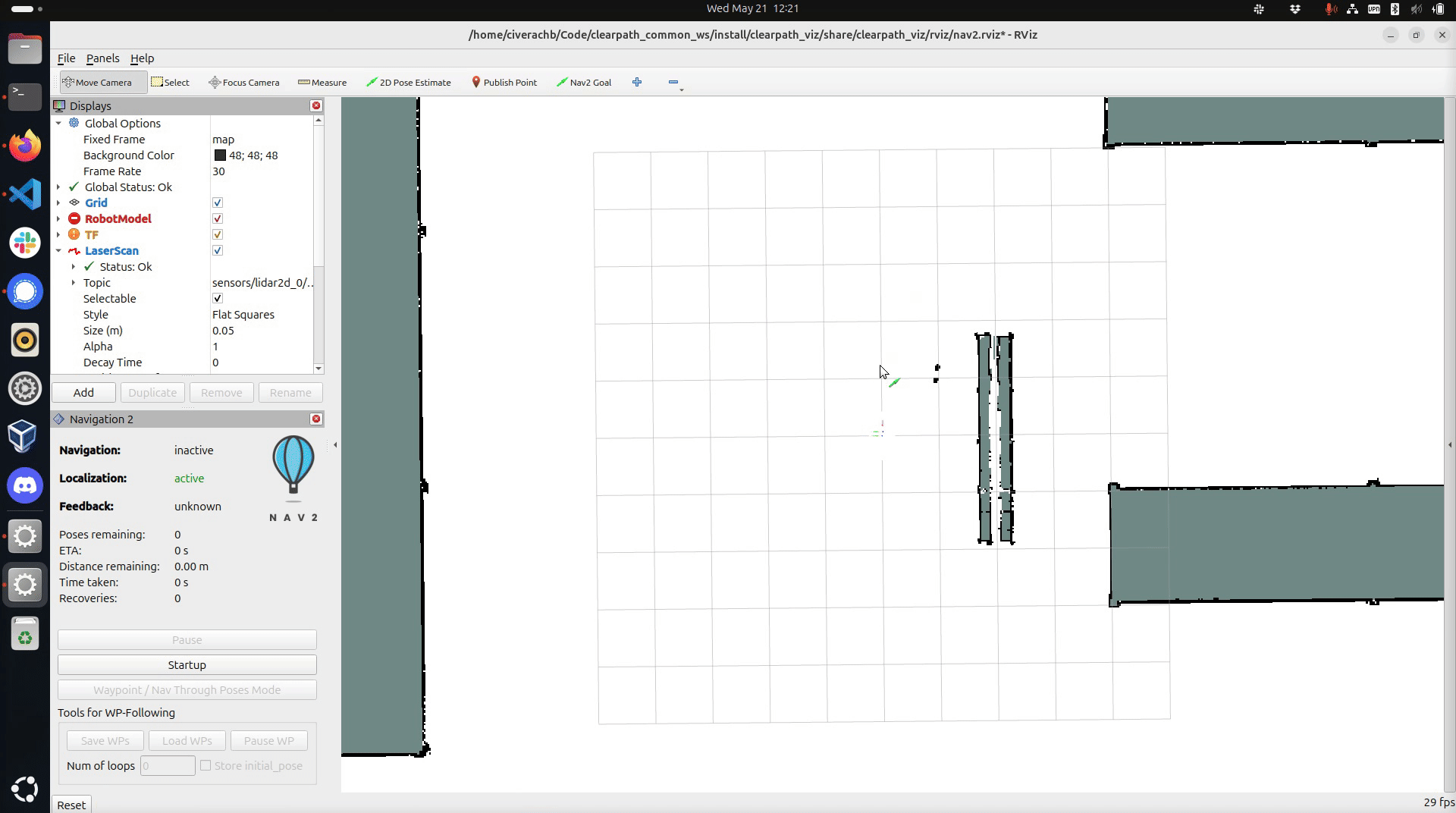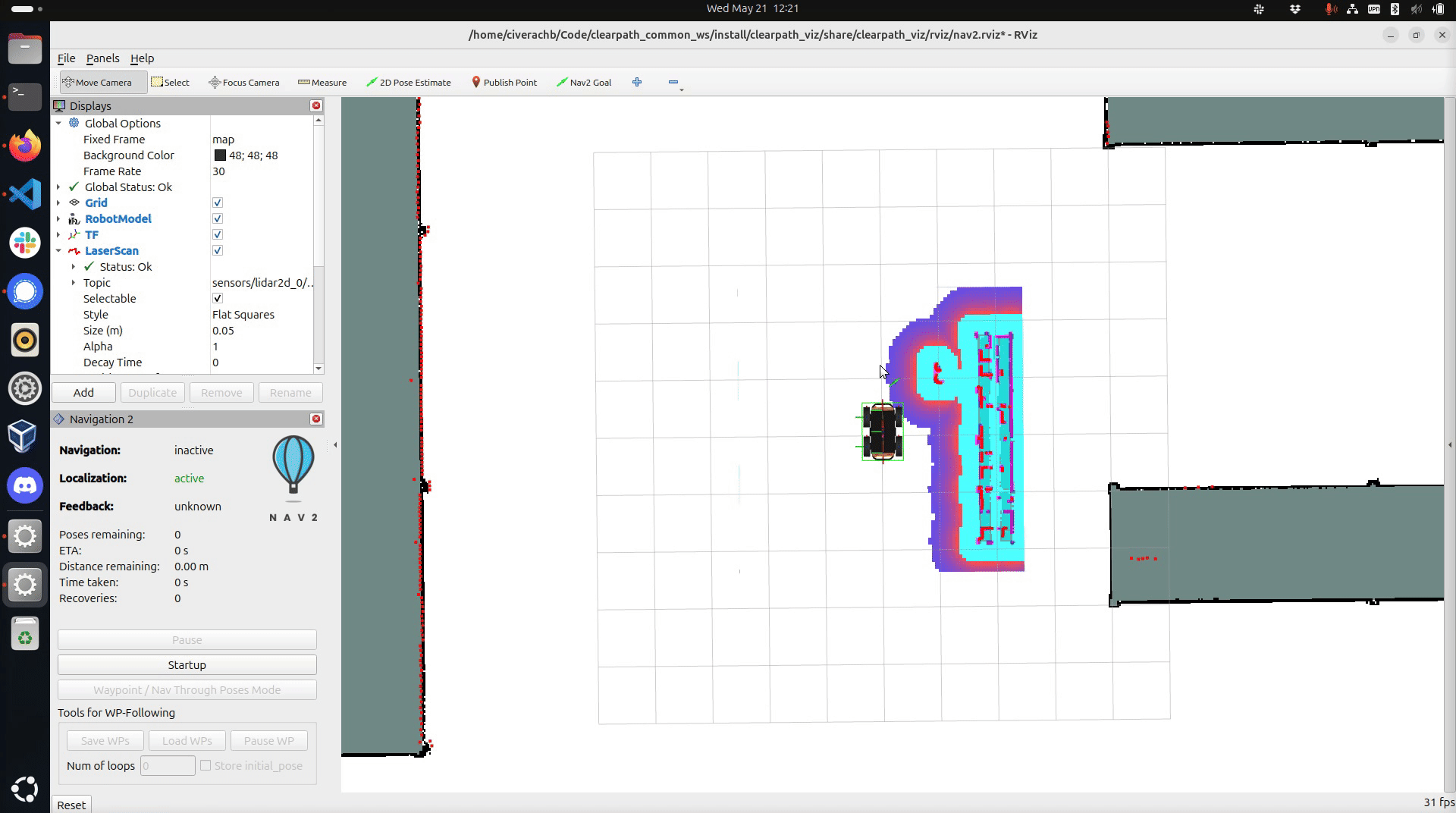
If you are using SLAM and there is no map yet, simply click on the centre of the screen and drag up.
Once you have set the robot's initial pose you should see red markers representing the lidar data as well as coloured gradients indicating collision zones around walls and obstacles.